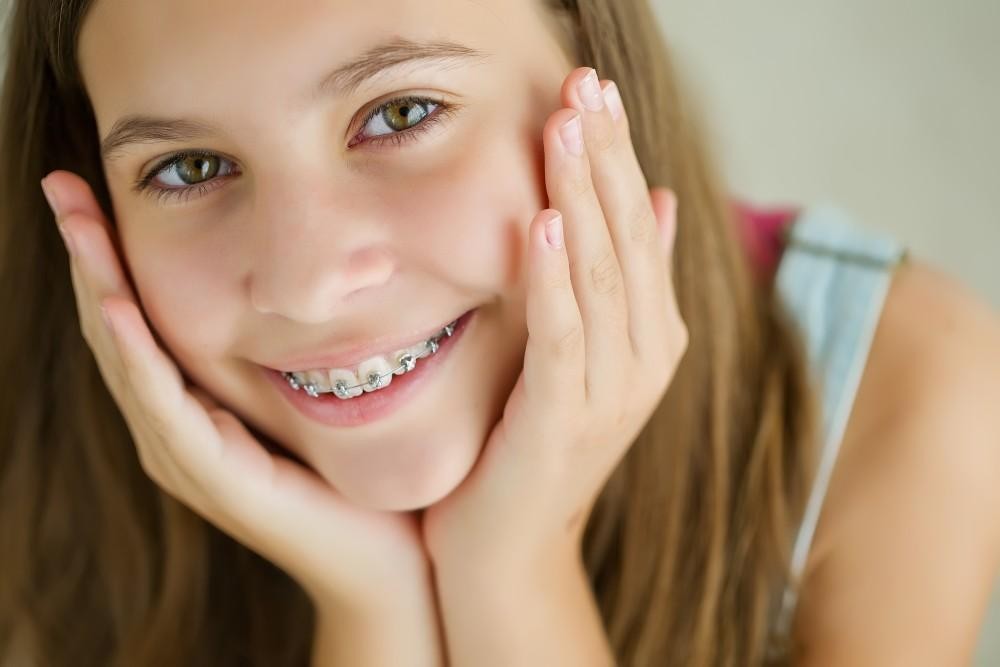
The Best Age for Your Child’s First Orthodontic Evaluation
What is the Best Age for a Child’s First Orthodontic Evaluation?
According to the American Association of Orthodontists (AAO), children should have their first orthodontic evaluation by age seven. This recommendation is based on the natural development of a child’s teeth and jaw at this stage. By age seven:
- Some permanent teeth have already emerged, allowing the dentist to examine the bite alignment.
- Early signs of malocclusion (bad bite), overcrowding, or jaw growth issues may be noticeable.
- While some children may need early intervention, others will be monitored for future treatment.
Why is an Early Orthodontic Evaluation Important?
Early evaluations by a pediatric dentist in provide several benefits:
- Detecting Issues Early – Orthodontists can spot potential problems with jaw growth, teeth alignment, and bite issues before they become severe.
- Guiding Jaw Development – If a child’s jaw is not developing properly, early treatment can guide growth and prevent the need for extensive correction later.
- Reducing the Need for Extractions – Early intervention can sometimes prevent overcrowding and the need for permanent tooth extractions later on.
- Improving Speech and Chewing Functions – Misaligned teeth can affect speech clarity and chewing efficiency.
- Boosting Confidence – Early orthodontic treatment can correct visible dental issues, giving your child a boost in self-confidence.
Signs That Your Child May Need an Early Orthodontic Assessment
Even if your child is under seven, certain warning signs may indicate the need for an orthodontic evaluation:
✔️ Difficulty chewing or biting food
✔️ Thumb-sucking beyond age five
✔️ Crowded or misplaced teeth
✔️ Mouth breathing instead of nose breathing
✔️ A jaw that seems too far forward or backward
✔️ Early or late loss of baby teeth
✔️ Speech difficulties related to dental alignment
If you notice any of these signs, it’s best to schedule an orthodontic consultation with a pediatric dentist in to ensure your child’s oral health is on track.
What Happens During the First Orthodontic Visit?
A pediatric dentist or orthodontist will conduct a comprehensive evaluation, including:
- Visual Examination – Checking the growth and alignment of your child’s teeth and jaw.
- X-Rays – Providing a detailed look at the development of permanent teeth beneath the gums.
- Bite Analysis – Assessing how the upper and lower teeth fit together.
- Treatment Planning – If intervention is needed, the dentist will discuss options, including braces, space maintainers, or other orthodontic appliances.
Does Every Child Need Braces After Their First Evaluation?
Not necessarily! The purpose of an early orthodontic checkup is to identify issues early. Some children may not need immediate treatment, but regular monitoring ensures that orthodontic concerns don’t develop into larger problems.
For children who do need early intervention, options such as palatal expanders or partial braces can help guide dental development and reduce the severity of future orthodontic treatment.
Signs That Your Child Might Need Early Orthodontic Treatment
Here are some common dental and facial development concerns that should not be ignored:
1. Crowded, Crooked, or Misaligned Teeth
- If your child’s teeth appear overlapping, twisted, or out of alignment, it could be a sign of crowding.
- Early detection allows for treatment options that can guide teeth into the correct position, preventing severe crowding later.
2. Difficulty Chewing or Biting Food
- If your child frequently struggles to chew food properly, misaligned teeth or bite issues may be the cause.
- Difficulty biting into apples, sandwiches, or other firm foods can indicate problems with the jaw alignment or tooth positioning.
3. Thumb Sucking or Prolonged Pacifier Use Beyond Age 3
- While thumb sucking and pacifier use are common in infants, prolonged habits beyond age 3 can lead to:
- Open bites (when the front teeth don’t meet).
- Overbites (protruding front teeth).
- Changes in jaw structure that may require orthodontic correction.
4. Mouth Breathing and Snoring
- Chronic mouth breathing may indicate a narrow airway, improper jaw growth, or nasal obstructions.
- It can lead to dry mouth, increased risk of cavities, and improper facial development.
- Snoring in children can sometimes be a sign of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which should be evaluated by a specialist.
5. Protruding Front Teeth (Overbite)
- If the upper front teeth stick out too far over the lower teeth, it increases the risk of trauma or fractures.
- Early orthodontic intervention can help guide proper jaw development and reduce the severity of the overbite.
6. Jaw Shifting or Clicking When Opening/Closing the Mouth
- If your child’s jaw shifts to one side, clicks, or makes popping noises, it could be a sign of a developing jaw misalignment or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) issues.
- Orthodontic treatment may be needed to correct jaw positioning and prevent pain or dysfunction in the future.
What to Expect During the First Orthodontic Evaluation
Here’s what to expect during this initial visit:
1. Thorough Examination of Teeth and Jaw Alignment
- The dentist will visually examine your child’s teeth, bite, and jaw position to detect any early signs of misalignment, crowding, or bite issues.
- They will also check for overbites, underbites, crossbites, and spacing issues that could impact oral health.
2. X-Rays and Digital Scans to Assess Underlying Structures
- Dental X-rays provide a detailed view of tooth positioning, jawbone growth, and unerupted permanent teeth beneath the gums.
- Digital scans or 3D imaging may be used to capture precise images of the teeth and jaw for more accurate treatment planning.
3. Discussion of Potential Treatments
- The pediatric dentist or orthodontist will explain whether immediate intervention is needed or if your child’s development should be monitored over time.
- If early treatment is recommended, options may include:
- Braces to correct misaligned teeth.
- Spacers to maintain space for incoming permanent teeth.
- Palatal expanders to address jaw development concerns.
- If no immediate action is necessary, the dentist may suggest regular check-ups to monitor your child’s dental growth.
4. Personalized Recommendations Based on the Child’s Growth Stage
- The dentist will provide customized advice based on your child’s specific needs, including dental hygiene tips, diet recommendations, and follow-up visit schedules.
- If orthodontic treatment is expected in the future, they will outline a treatment timeline to help parents prepare for the next steps.
Orthodontic Treatment Options for Kids
Here are some common options:
1. Braces (Traditional or Clear Options for Bite Correction)
- Braces are the most well-known orthodontic treatment for correcting misaligned teeth, overcrowding, and bite issues.
- Options include:
- Traditional metal braces – Durable and effective for complex cases.
- Clear ceramic braces – Less noticeable but work similarly to metal braces.
- Braces apply gentle pressure to gradually move teeth into their proper positions.
2. Palatal Expanders to Widen the Upper Jaw and Create Space
- Some children have a narrow upper jaw, which can lead to crowding or crossbites.
- A palatal expander helps widen the jaw by gradually applying pressure to create more space for permanent teeth.
- This treatment is most effective in younger children while their jawbones are still developing.
3. Retainers for Minor Adjustments and Maintaining Alignment
- Retainers are typically used after braces to keep teeth in their corrected positions.
- In some cases, retainers may be used as a standalone treatment for minor tooth movement or alignment issues.
- Removable and fixed retainers are available, depending on the child’s needs.
4. Space Maintainers if Baby Teeth Are Lost Too Early
- If a child loses a baby tooth too soon, the surrounding teeth may shift, leading to spacing issues.
- Space maintainers hold the space open until the permanent tooth emerges, preventing misalignment.
- These are especially useful in preventing the need for future orthodontic treatments.